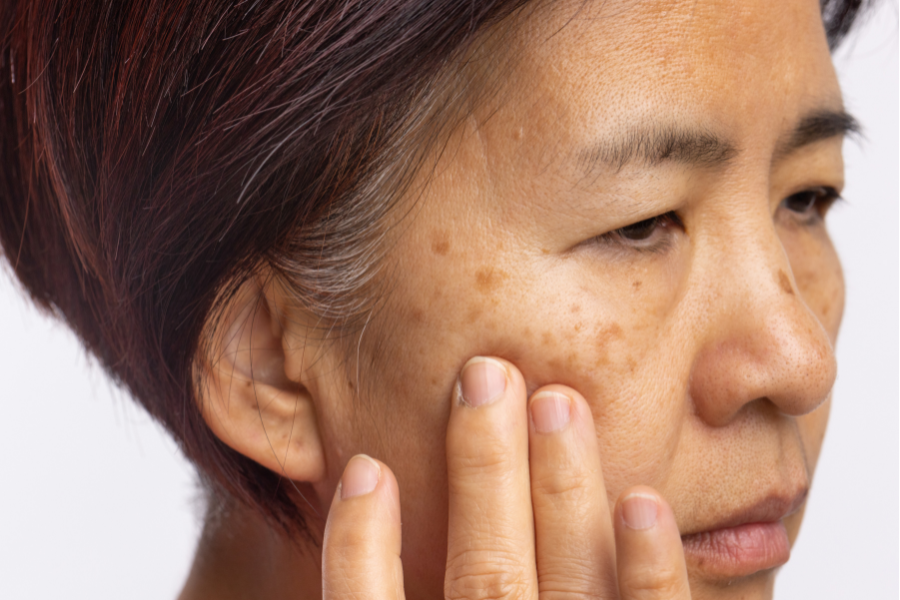
Melanin pigmentation, also known as age spots, is a common skin concern for many women. It is caused by a variety of factors, including prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation, environmental pollution, and stress, which can accelerate melanin production and lead to spots on the skin. NeoYouth will explore methods to prevent and improve melanin pigmentation, helping you maintain healthy skin.
What is melanin deposition? How is it formed?
Melanin deposition refers to the appearance of darker spots or patches in certain areas of the skin due to excessive production or uneven distribution of melanin. Melanin is a natural pigment, mainly produced by melanocytes, and plays a protective role in the skin, preventing damage from ultraviolet rays. However, when the skin is affected by factors such as ultraviolet rays, external stimuli, or endocrine disorders, melanocytes are activated, producing more melanin as a protective mechanism. If this melanin is not smoothly eliminated through skin metabolism, it will accumulate in the epidermis, forming age spots, dark spots, or uneven skin tone.
Types of Melanin Deposition: Understanding Different Types of Pigmentation
Based on the depth, form, and cause of the deposits, melanin deposition can be classified into several types, including:
Surface pigmentation
Melanin is mainly deposited in the epidermis, appearing lighter in color and with clear borders. Common types include freckles, sunspots (sun spots), and age spots. Freckles are mostly small, irregular, light brown spots, commonly found on sun-exposed areas such as the cheeks and bridge of the nose. Sunspots are larger, darker, round patches, usually appearing on the forehead and cheekbones. Age spots are mostly raised, rough, yellowish-brown or black patches, related to skin aging and prolonged sun exposure.
Deep pigmentation
Melanin deposits in the dermis, resulting in a darker color and indistinct borders, making them stubborn and difficult to lighten. Common types include hormonal melasma (liver spots), zygomatic nevus, and dark spots (Ota spots). Hormonal melasma is more common in women, presenting as symmetrically distributed dark brown patches caused by hormonal changes. Zygomatic nevus is caused by excessive proliferation of dermal cells, resulting in a darker color and often appearing on the cheekbone area. Dark spots are bluish-gray or bluish-black, mostly congenital, and distributed on one side of the face.
Mixed pigmentation
This refers to pigmentation where melanin is present in both the epidermis and dermis, resulting in a darker color and greater difficulty in treatment, such as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and some types of melasma. These types of pigmentation are usually caused by skin inflammation, injury, or hormonal fluctuations, and the pigmentation layers are complex, requiring a combination of different treatment methods.
Common locations of melanin deposition
Melanin deposition often occurs in areas of thinner skin that are more susceptible to UV exposure or friction, specifically including:
- Face: The cheeks, forehead, bridge of the nose, upper eyelids, and around the eyes are the most common areas for pigmentation. The skin around the eyes is thin and prone to developing pigmented dark circles; the forehead and cheeks are prone to sunspots and hormonal spots due to prolonged sun exposure. The chin area is more often affected by hormonal changes or friction, leading to pigmentation.
- Other parts of the body: The armpits, genitals, and buttocks are prone to melanin deposition due to prolonged friction; legs frequently exposed to the sun or wearing shorts are also more likely to develop age spots. In addition, exposed areas such as the neck and back of the hands are also prone to pigmentation due to ultraviolet radiation and aging.
- Special cases: After skin damage or inflammation, such as acne, eczema, burns, etc., post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation often remains, forming spots of varying shades.
Causes of melanin deposition
First, we need to understand the causes of melanin deposition in the skin. The following are the most common main factors contributing to the formation of dark spots:
Sun exposure
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is one of the most common causes of melanin deposition. Exposure to UV rays can stimulate melanocytes to produce more melanin, especially in areas of skin that are frequently exposed to the elements.
Damaged skin
When the skin's surface is damaged by acne, the affected area may turn dark red or light brown, a sign of melanin deposition. To accelerate the repair process, the skin will secrete more melanin in the damaged area, which gradually accumulates over time and forms light-colored spots.
drug
Certain medications, such as those for mental illnesses, allergies, epilepsy, and pain, may increase melanin production, leading to gray or brownish-gray circular spots on the skin, or even linear melanin deposits. Therefore, it is advisable to consult a doctor while taking any medication to determine if it will affect skin health.
disease
Many diseases can cause pigmentation. For example, obesity or diabetes can lead to darkening and roughness of the skin in areas such as the armpits or back of the neck due to high insulin levels in the blood; this condition is called acanthosis nigricans. Additionally, kidney dysfunction can also stimulate melanin production, resulting in darker skin. If you experience unexplained pigmentation, you should consult a doctor for diagnosis.
Hormonal changes
Pregnancy or the use of hormone-containing medications can cause hormonal changes that can increase melanocyte activity, leading to age spots.
Lifestyle factors
Stress and staying up late can affect skin health and indirectly promote melanin production.
Genetic factors
Due to genetic factors, some people are more prone to melanin deposition.
How to prevent melanin deposition?
If you do not have pigmentation issues, you can take measures to prevent melanin deposition based on the above reasons:
- Sun protection: Avoid prolonged sun exposure and use sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher every day, regardless of whether it is sunny or cloudy.
- Healthy diet: Consume foods rich in antioxidants, such as blueberries, green tea, and tomatoes. These foods help fight free radicals and reduce damage to the skin.
- Sufficient sleep and stress reduction: Ensure you get enough sleep every day and take appropriate measures to reduce life stress.
Methods to improve melanin pigmentation – starting with daily skincare.
- Topical whitening products: Choose whitening products containing ingredients such as vitamin C, arbutin, and licorice extract, as these ingredients can inhibit melanin production.
- Chemical exfoliation: Use products containing fruit acids or salicylic acid to help promote epidermal cell renewal and lighten existing pigmentation.
- Keep your skin moisturized: Dry skin is more susceptible to environmental stress, and proper moisturizing can protect the skin from external damage.
- Professional treatment: In addition, laser treatment and other methods can reduce pigmentation in a targeted manner, but they should be carried out under the guidance of a professional.
- Internal health supplements: To improve pigmentation problems from the inside out, such as health supplements including vitamin A, vitamin E, vitamin B3 and B12, vitamin K2, glutathione, etc. These ingredients can help fight oxidation, regulate melanin production, reduce dark spots and promote skin health.
Made in Japan, 100% pure NMN anti-aging formula
Through the methods described above, we can not only prevent the formation of melanin deposits, but also effectively lighten and improve pigmentation, resulting in a brighter and more even skin tone. For further enhancement, it can be used in conjunction with NeoYouth's NMN anti-aging formula nutritional supplements and Merrillady, a Japanese skincare product , to further improve pigmentation issues, continuously providing hydration, brightening, anti-inflammatory, spot-fading, yellowing-reducing effects, and protection against oxidation by a factor of 1 million. It also has anti-aging, skin-beautifying, and body-reversing effects.
NeoYouth's highly effective anti-aging formula contains 100% pure NMN, offering anti-aging and beautifying effects while comprehensively enhancing bodily functions. It activates sirtuins, helping to eliminate free radicals and reduce oxidative stress. Long-term use helps maintain radiant, elastic skin and reduces fine lines.
Furthermore, excessive UV exposure reduces NAD+ levels in the skin, accelerating the aging process and causing dull, uneven skin tone. NMN supplement capsules contain 50 mg each of resveratrol and coenzyme Q10, which can protect skin cells from UV damage, inhibit melanin production, promote collagen production and improve skin elasticity, repair damaged cells, and reduce UV damage, thus slowing down skin aging.
To address pigmentation, it's essential to change daily habits, use appropriate whitening products to prevent melanin deposition, avoid excessive sun exposure, and seek professional medical help when necessary. Understanding the causes and solutions for melanin deposition can help us combat skin aging more effectively. By combining these methods with the assistance of NMN nutritional supplements, pigmentation can be effectively improved.
References:
- https://www.amiino.com.tw/blog/posts/%E7%9A%AE%E8%86%9A%E9%BB%91%E8%89%B2%E7%B4%A0%E6%B2%89%E6%BE%B1
- https://www.jomay.com.tw/news_detail/68.htm